
 Data Download
Data Download
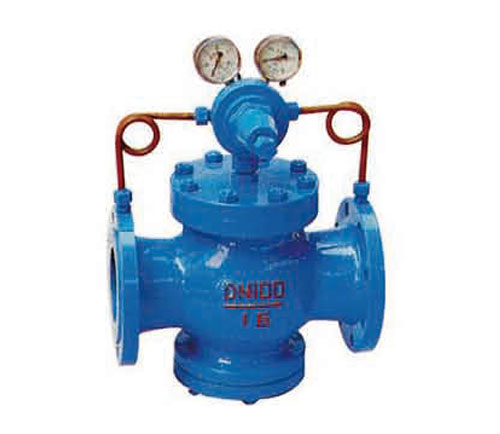
The piston type gas relief valve is composed of two parts, the main valve and the pilot valve. The main valve is mainly composed of seat, main disc, piston, spring and other parts. The guide valve is mainly composed of seat, disc, diaphragm, spring, adjusting spring and other parts. The outlet pressure is set by adjusting the spring pressure, the diaphragm is used to sense the outlet pressure change, and the pilot valve opens and closes to drive the piston to adjust the flow area of the throttle part of the main valve, so as to realize the function of reducing pressure and stabilizing pressure.
Application scope
Piston gas pressure relief valve products are mainly used in gas pipelines, such as air, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, liquefied gas, natural gas and other gases.
Working principle
When the pressure relief valve leaves the factory, the regulating spring is in the uncompressed state. At this time, the main valve disc and the secondary valve disc are in the closed state. When used, the regulating screw is rotated clockwise, and the regulating spring is compressed, so that the diaphragm is moved down and the auxiliary valve disc is opened. The medium enters the top of the piston, and the piston moves downward to push the main valve disc under the action of the medium pressure. Leaving the main seat, the medium flows to the valve and enters under the diaphragm at the same time. When the pressure behind the valve exceeds the setting pressure, the diaphragm is pushed up to compress the regulating spring. The secondary valve disc moves towards the closing direction, which reduces the medium flowing into the piston and reduces the pressure. At this time, the main valve disc moves up and down under the spring force of the main valve disc, which reduces the gap between the main valve disc and the main seat, reduces the medium flow rate, and reduces the pressure behind the valve to a new balance. On the contrary, when the pressure behind the valve is low. When the pressure is adjusted, the clearance between the main disc and the main seat increases, and the medium flow increases, so that the pressure behind the valve increases to a new balance.
Standard specification
Design and Manufacture Standard: GB12246
Structural Length Standard: GB/T 12221-2005
Connection Flange Standard: GB/T 9113
Pressure and temperature grade: GB/T 12224-2005
Standard for test and inspection: GB/T 13927-2008
Copyright©Vesey Control Technical Support;PRCVM
